Head Medical Consultant & Patient Care at UniquEra Clinic
A receding hairline rarely feels like a small change. It starts quietly. One day you notice your temples look a little higher in photos. Another day, styling your hair takes longer than it used to. Over time, that subtle shift turns into something harder to ignore. For many people, it affects confidence long before it becomes obvious to others.
Receding hairlines affect both men and women, but the experience, pattern, and treatment approach are often very different. What matters most is understanding why it’s happening, what stage you’re at, and which hair loss treatment for receding hairline actually works for your situation, rather than chasing generic solutions.
This guide breaks it all down. Causes. Differences between men and women. Non-surgical and surgical treatments. Timelines. And when a hair transplant for receding hairline becomes the right option.
A receding hairline refers to the gradual thinning or backward movement of hair along the frontal scalp; a process mediated by complex hormonal and genetic factors. It most commonly begins at the temples, creating an “M” shape in men. In women, it usually manifests as overall thinning at the front or widening of the natural part rather than sharp temple recession.
The most common cause is androgenetic alopecia; a hereditary condition where hair follicles become increasingly sensitive to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a metabolite of testosterone. DHT binds to androgen receptors in genetically susceptible follicles, triggering a process called follicular miniaturization. Over months and years, affected follicles progressively shrink, produce thinner hair shafts, and eventually enter permanent dormancy.
This process occurs in phases:
Beyond genetics and hormones, several factors can accelerate or trigger hairline recession:
Early identification is critical. The earlier a receding hairline is diagnosed and addressed, the more treatment options remain viable and the better the potential outcomes.
| Aspect | Men | Women |
| Pattern | Clear temple recession forming “M” or “U” shape | Diffuse frontal thinning, widening part, less defined recession |
| Classification | Norwood-Hamilton Scale (Stages I-VII) | Ludwig Scale or Frontal Accentuation Pattern |
| Primary Cause | DHT sensitivity (androgenetic alopecia) | Multiple factors: hormones, iron, thyroid, genetics |
| Age of Onset | Often begins 20s-30s | Usually post-menopausal, but can occur earlier |
| Progression | Predictable, often steady advancement | Variable, may stabilize or fluctuate with hormonal changes |
| Crown Involvement | Common as pattern advances | Less common; more diffuse overall thinning |
| Transplant Candidacy | Typically excellent due to defined pattern | Requires careful evaluation; success depends on donor density and diffuse thinning extent |
The answer depends on why the hairline is receding and how advanced it is.
No treatment can permanently “cure” genetic hair loss. The goal is control, restoration, and long-term planning.
Minoxidil & Finasteride
Some people consider topical or oral medications. These may help slow hair loss but come with limitations. These FDA-approved medications are widely used, but:
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma)
UniquEra prefers PRP as a regenerative option. It involves:
Protocols usually involve:
It pairs well with hair transplant for faster recovery and denser regrowth.
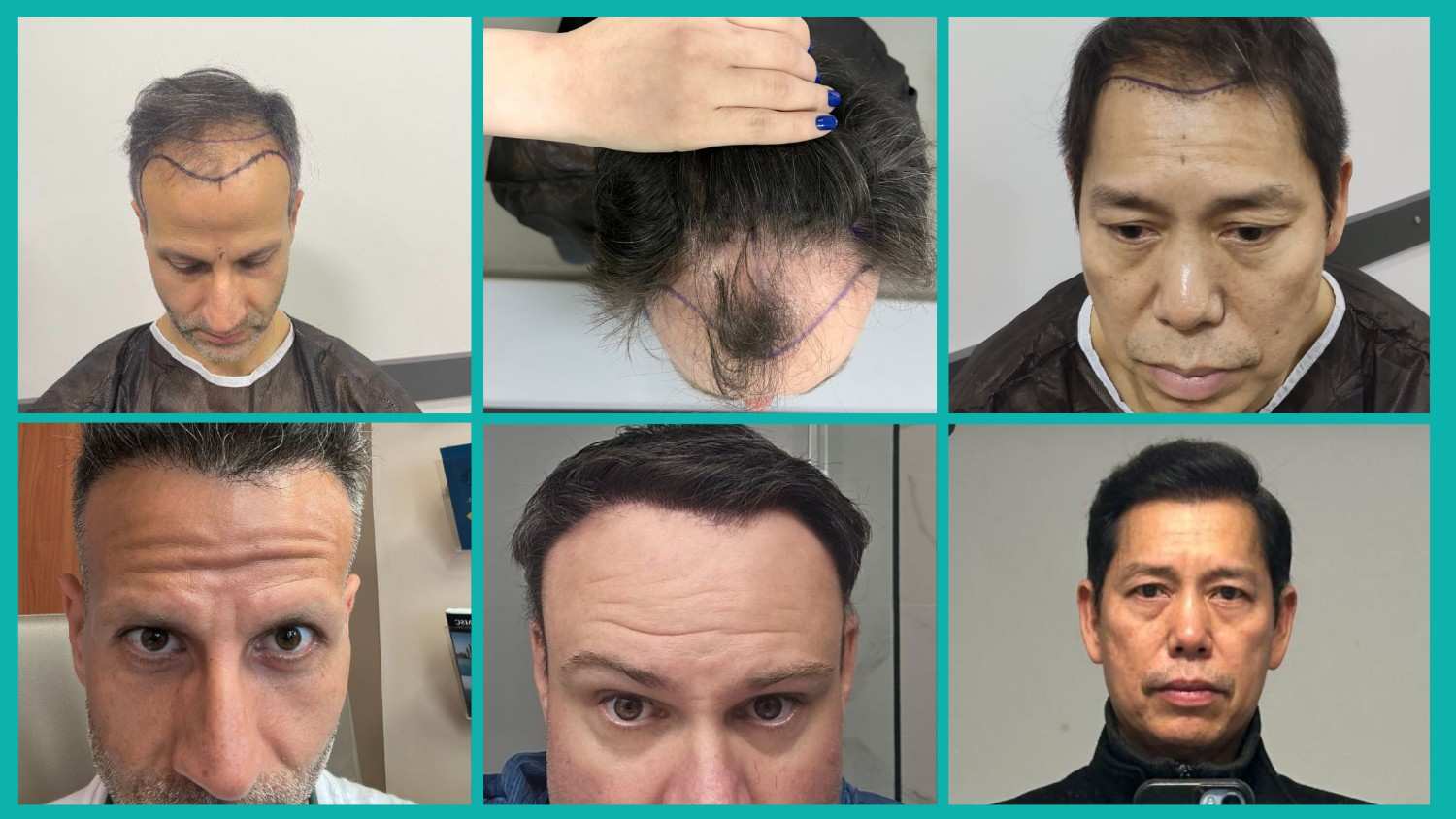
When follicular miniaturization has progressed beyond medical salvage, or when patients desire immediate, definitive restoration, hair transplantation provides the gold standard permanent solution.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Hair transplantation is based on a principle called donor dominance: follicles harvested from the occipital and parietal scalp (back and sides) are genetically programmed to resist DHT effects. When relocated to the receding hairline, they maintain these characteristics and continue growing permanently.
Optimal candidates meet several criteria:
Both men and women can be candidates, though evaluation criteria differ based on the diffuse versus patterned nature of loss.
In practice, many clinics use a hybrid approach, selecting the technique based on anatomy, density goals, and coverage area rather than promoting a single method.
Main Techniques:
| Feature | FUE | DHI |
| Extraction | Micro-punch tool | Micro-punch tool |
| Implantation | Incisions then grafts placed manually | Grafts implanted with Choi pen |
| Scarring | Tiny dot scars | Tiny dot scars |
| Shaving | Usually required | Can be done with partial/no shave |
| Ideal For | General thinning | Precise hairline, small areas |
| Recovery | 7–10 days | 7–10 days |
The best treatment for receding hairline often involves a multimodal approach. Many patients achieve superior results by combining surgical and non-surgical options. For example, undergoing a hair transplant while maintaining a regimen of minoxidil and finasteride can help preserve existing hair while enhancing transplanted hair growth.
Similarly, complementing a hair transplant with PRP therapy can accelerate healing, improve graft survival, and stimulate dormant follicles in the surrounding areas. Your hair restoration specialist can design a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific pattern of hair loss and aesthetic goals.
| Timeline | Hair Transplant (FUE/DHI) |
| Days 1-3 | Scabbing begins, mild swelling |
| Days 4-10 | Scabs shed, healing progresses |
| Weeks 2-4 | Shock loss (transplanted hairs shed-normal) |
| Months 3-4 | New growth begins |
| Months 6-9 | Visible improvement, 60-70% density |
| Months 12-18 | Final result, full density and maturation |
Transplanted hair grows permanently. However, surrounding native hair may continue thinning if androgenetic alopecia isn’t medically managed with PRP or medications.
Regardless of which treatment you choose, protecting your existing hair is essential for long-term success. Consider these preventive measures:
Costs depend on:
Many patients choose hair transplant surgery in Turkey due to access to experienced medical teams and comprehensive care at significantly lower overall cost compared to Western countries, without compromising medical standards.
At UniquEra Clinic, treatment planning focuses on:
The UniquEra clinic follows a team-based medical model, where planning, extraction, implantation, and aftercare are handled by experienced professionals who have worked together for years. Technique selection is based on patient anatomy and goals, not marketing preference.
Choosing the best hair loss treatment for receding hairline in turkey depends on multiple factors including the extent of hair loss, your age, overall health, budget, and personal preferences. A thorough consultation with a hair restoration specialist is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
During your consultation, expect a comprehensive scalp examination, discussion of your medical history, evaluation of hair loss patterns, and review of all suitable treatment options. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about success rates, potential side effects, recovery times, and long-term maintenance requirements.
A receding hairline doesn’t have to be a permanent concern. With today’s advanced treatment options ranging from FDA-approved medications and innovative PRP therapy to state-of-the-art hair transplant techniques, effective solutions exist for both men and women experiencing hairline recession.
By taking action now and choosing the right treatment path, you can restore not just your hairline, but also your confidence and self-image.
If you’re ready to address your receding hairline, schedule a consultation at UniquEra clinic with a qualified hair restoration specialist to explore your options and begin your journey toward fuller, healthier hair. With the right treatment plan and expert guidance, achieving a natural-looking, youthful hairline is well within reach.
1. Can a receding hairline grow back naturally?
Only if the cause is temporary. Genetic hairline recession does not reverse without treatment.
2. What is the best treatment for receding hairline?
Early stages respond well to PRP. Advanced stages require hair transplant for visible restoration.
3. Is hair transplant permanent?
Yes. Transplanted follicles are resistant to hair loss and grow permanently. Read more about Is hair transplant permanent?
4. Can women get a hair transplant for receding hairline?
Yes, in suitable cases. Evaluation is essential to determine the right approach.
5. When should I consider a hair transplant for my receding hairline?
Consider hair transplant when medications haven’t achieved desired density restoration, your hair loss pattern has stabilized, you have sufficient donor hair, and you want permanent, significant improvement. Consultation with a specialist determines your candidacy.
6. How long does it take to see results from receding hairline treatment?
Medications require 6-12 months for visible improvement. PRP shows results after 2-3 sessions (3-6 months). Hair transplant takes 12-18 months for full results, with initial growth visible around month 4. Patience and consistent treatment are essential.
7. Is PRP effective for receding hairline?
Clinical studies show PRP improves density and thickness in early-stage androgenetic alopecia. Results vary but many patients experience improvement, especially when combined with proper scalp care.
8. Does a hair transplant for receding hairline look natural?
When performed by experienced specialists using modern FUE or DHI techniques with proper hairline design, hair transplant results look completely natural. The key is irregular, soft hairline edges with appropriate angle and direction, avoiding straight “planted” appearance.
9. Will I have scars after a receding hairline transplant?
Modern FUE and DHI techniques leave tiny dot scars (under 1mm) that are virtually invisible, even with very short hair. FUT creates a linear scar requiring longer hair coverage. UniquEra specializes in minimal-scarring techniques for maximum styling flexibility.
10. Do I have to stay on medication after a hair transplant?
Transplanted hair is permanent and doesn’t require medication to survive. However, continuing finasteride and/or minoxidil is often recommended to protect non-transplanted hair from progressive miniaturization, maximizing your overall long-term density.